반응형
1. Shapely로 Geometry 생성하기
- Polygon 생성하기(튜플)
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
p1 = Polygon(((1,2), (5,3), (5,7), (1,9), (1,2)))
p1
p2 = Polygon(((6,6), (7,6), (10,4), (11,8), (6,6)))
p2
- Point생성하기(좌표값)
from shapely.geometry import Point
point = Point(2.0, 2.0)
point
- Line 생성하기
from shapely.geometry import LineString
line = LineString([(0,0), (10,10)])
line
- Linear Ring 생성하기
from shapely.geometry.polygon import LinearRing
ring = LinearRing([(0,0), (3,3), (3,0)])
ring
- MultiPoint 생성하기
from shapely.geometry import MultiPoint
points = MultiPoint([(0,0), (3,3)])
points
- MultiLine 생성하기
from shapely.geometry import MultiLineString
coords = MultiLineString([((0,0), (1,1)),((-1,0), (1,0))])
coords
- MultiPolygon 생성하기
from shapely.geometry import MultiPolygon
polygons = MultiPolygon([p1,p2])
polygons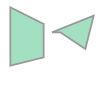
2. Shapely 공간 함수
# 면적 구하기
print(p1.area)
# 경계 구하기
print(p1.bounds)
# 길이 구하기
print(p1.length)
# geometry Type 구하기
print(p1.geom_type)22.0
(1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 9.0)
19.59524158061724
Polygon3. Shapely로 JSON Geometry 읽기
- Json 파일 생성 및 shape를 이용해 로딩
import json
from shapely.geometry import mapping, shape
jData = json.loads('{"type":"Polygon","coordinates":[[[1,1],[1,3],[3,3]]]}')
p = shape(jData)
p
- geometry를 json형태로 변환
mapping(p){'type': 'Polygon', 'coordinates': (((1.0, 1.0), (1.0, 3.0), (3.0, 3.0), (1.0, 1.0)),)}4 Fiona 데이터 읽기
- shp 파일 정보 표출
print(len(c))
print(c.driver)
print(c.crs)100
ESRI Shapefile
{'proj': 'tmerc', 'lat_0': 38, 'lon_0': 127, 'k': 1, 'x_0': 200000, 'y_0': 600000, 'ellps': 'GRS80', 'units': 'm', 'no_defs': True}- shp 파일 데이터 읽기
import fiona
c = fiona.open(r'data/node.shp')
rec = next(iter(c))
print('keys = ', rec.keys())
print('type = ', rec['type'])
print('prop = ', rec['properties'])
print('id = ', rec['id'])
print('geom = ', rec['geometry'])keys = dict_keys(['type', 'id', 'properties', 'geometry'])
type = Feature
prop = OrderedDict([('NODE_ID', '1100025100'), ('NODE_TYPE', '101'), ('NODE_NAME', '하계5,6단지앞교차로'), ('TURN_P', '1'), ('REMARK', None)])
id = 0
geom = {'type': 'Point', 'coordinates': (205838.0880999937, 559449.3750999967)}5 데이터 다루기
- shape file 읽고 첫 번째 Feature 정보 가져오기
import fiona
with fiona.open(r'data/node.shp') as src:
print(src[0]){'type': 'Feature', 'id': '0', 'properties': OrderedDict([('NODE_ID', '1100025100'), ('NODE_TYPE', '101'), ('NODE_NAME', '하계5,6단지앞교차로'), ('TURN_P', '1'), ('REMARK', None)]), 'geometry': {'type': 'Point', 'coordinates': (205838.0880999937, 559449.3750999967)}}참고
- 파이썬을 활용한 지리공간 분석 마스터하기
- 예제는 국가표준노드링크로 진행
반응형
'GIS > Python 기반 공간 분석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 벡터 데이터 분석-3. geopandas (0) | 2021.04.09 |
|---|---|
| 벡터 데이터 분석-1. OGR (0) | 2021.04.09 |
| 공간 데이터 타입 (0) | 2021.03.21 |
| 파이썬으로 postgresql(postGIS) 사용하기 (0) | 2021.03.20 |
| GIS 라이브러리 소개 및 설치 (0) | 2021.03.18 |